Schema Maintenance
- “A schema is an abstract representation of the distinctive characteristics of an event, a kind of blueprint of its most salient elements.”
- “[A schema is] an abstract cognitive plan that serves as guide for interpreting information and solving problems.”
- “[A schema is] any broad organizing principle for making sense of one’s life experience.”
Abandonment
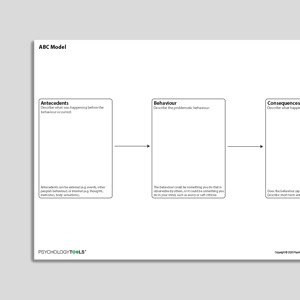
ABC Model
Anxiety - Self-Monitoring Record
Approval-/Admiration-Seeking
Attention Training Experiment
Behavioral Experiment
Behavioral Experiment (Portrait Format)
Belief Driven Formulation
Belief-O-Meter (CYP)
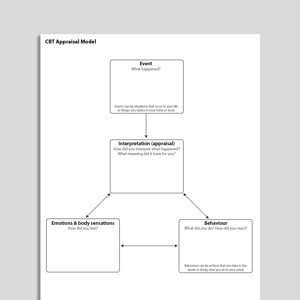
CBT Appraisal Model
CBT Thought Record Portrait
Challenging Your Negative Thinking (Archived)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Depersonalization (Hunter, Phillips, Chalder, Sierra, David, 2003)
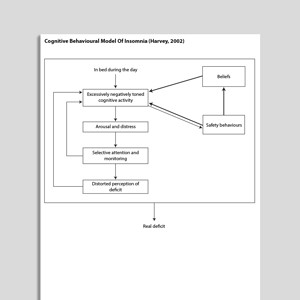
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Insomnia (Harvey, 2002)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD: Ehlers & Clark, 2000)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Social Phobia (Clark, Wells, 1995)
Coping Styles And Responses (Schema Therapy)
Core Belief Magnet Metaphor
Court Trial Thought Challenging Record (Archived)
Critical Care And PTSD
Critical Illness Intensive Care And Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Defectiveness
Embracing Uncertainty
Emotional Deprivation
Emotional Inhibition
How Your Past Affects Your Present (CBT)
How Your Past Affects Your Present (Schema Therapy)
Intolerance Of Uncertainty
Mental Filter
Modifying Rules And Assumptions
Overcoming Depression (Second Edition): Therapist Guide
Overcoming Depression (Second Edition): Workbook
Pie Charts (Archived)
Positive Belief Record
Process Focused Case Formulation
Reciprocal CBT Formulation
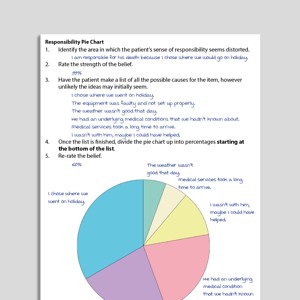
Responsibility Pie Chart
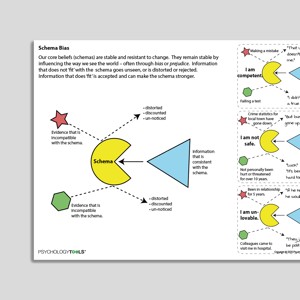
Schema Bias
Schema Formulation
Schema Metaphors
Social Anxiety Formulation
Thought Record – Courtroom Trial
Uncertainty Beliefs – Experiment Record
Uncovering Your Deeper Beliefs
Understanding Depression
Understanding Social Anxiety
Unmet Emotional Needs
What Are Safety Behaviors?
What Are Schemas?
What Keeps Depression Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
What Keeps Social Anxiety Going?
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Recommended Reading
- Beck, A.T. (1967). Depression: Causes and treatment. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press).
- James, I. A., & Barton, S. (2004). Changing core beliefs with the continuum technique. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 32(04), 431-442 archive.org
- Kovacs, M., & Beck, A. T. (1978). Maladaptive cognitive structures in depression. American Journal of psychiatry, 135(5), 525-533 archive.org
- Padesky, C. (1991). Schema as self-prejudice. International Cognitive Therapy Newsletter, 6, 6-7 archive.org
- Wenzel, A. (2012). Modification of core beliefs in cognitive therapy. Standard and innovative strategies in Cognitive Behavior Therapy, 17-34
What Is Schema Maintenance?
Young, Klosko, and Weishaar (2003) describe how “schemas begin in early childhood or adolescence as reality-based representations of the child’s environment.” Schemas continue to be elaborated upon throughout the course of our life, and then superimposed on later life experiences even when they are no longer applicable. For example, if a child formed an accurate schema during childhood that “other people are scary and unpredictable” then they may live with the emotional and behavioral consequences of this schema even if they live in a substantially different context as an adult.
An important property of schemas is that they strive for ‘cognitive consistency’—that we prefer to maintain a stable view of ourselves and the world, even if this schema is inaccurate.
“Early maladaptive schemas fight for survival … although it causes suffering, it is comfortable and familiar, it feels right” (Young, Klosko, & Weishaar, 2003).
Schemas are a key maintenance factor in cognitive therapy because they determine “what we notice, attend to, and remember of our experiences” (Padesky, 1994). A schema of ‘I’m bad’ may make it hard for an individual to notice when they do something good, leading to the maintenance of the unhelpful way of thinking and being. Mechanisms by which schemas are maintained include:
- selective attention;
- selective memory;
- biased interpretation of ambiguous stimuli such as discounting contradictory information or by seeing the information as an exception to the schema.
Treatment Approaches That Target Schema Maintenance / Schema Change
Padesky (1994) describes a number of techniques within CBT which may be used to change schemas including:
- continuum methods to evaluate self/behavior on negative and adaptive continuum;
- positive data logs to collect disconfirmatory evidence;
- historical texts of schema;
- imagery techniques;
- psychodrama / role-play techniques.
References
- Padesky, C. A. (1994). Schema change processes in cognitive therapy. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 1(5), 267–278.
- Young, J. E., Klosko, J. S., & Weishaar, M. E. (2003). Schema therapy: A practitioner’s guide. New York: Guilford Press.