Perfectionism
Multiple definitions of perfectionism have been offered including:
“Those whose standards are high beyond reach or reason, people who strain compulsively and unremittingly towards impossible goals and who measure their own worth entirely in terms of productivity and accomplishment. For these people, the effort for excellence is self-defeating.” (Burns, 1980).
“Setting of excessively high standards for performance accompanied by overly critical self-evaluation” (Frost, Marten, Lahart, & Rosenblate, 1990)
it is associated with practical difficulties and negative emotional consequences, causing procrastination and anxiety;
it is associated with a range of disorders including obsessive compulsive disorder, social anxiety, panic, generalized anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, chronic fatigue, depression, bipolar, and suicidal ideation and behavior;
it may impede the treatment of such disorders;
it increases the risk of developing eating disorders and depression.
Vicious Cycle - Costs And Benefits
Vicious Cycle - Costs And Benefits
Am I Experiencing Perfectionism?
Am I Experiencing Perfectionism?
Identifying Your Demanding Standards
Identifying Your Demanding Standards
Exploring Your Demanding Standards
Exploring Your Demanding Standards
Evaluating Your Demanding Standards
Evaluating Your Demanding Standards
Performance And The Yerkes-Dodson Law
Performance And The Yerkes-Dodson Law
Recognizing Bulimia Nervosa
Recognizing Bulimia Nervosa
Recognizing Anorexia Nervosa
Recognizing Anorexia Nervosa
Discounting In Perfectionism – The Ratchet Effect
Discounting In Perfectionism – The Ratchet Effect
Demanding Standards – Living Well With Your Personal Rules
Demanding Standards – Living Well With Your Personal Rules
Perfectionism Self-Monitoring Record
Perfectionism Self-Monitoring Record
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Clinical Perfectionism (Shafran, Cooper, Fairburn, 2002)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Clinical Perfectionism (Shafran, Cooper, Fairburn, 2002)
What Keeps Perfectionism Going?
What Keeps Perfectionism Going?
What Keeps Bulimia Going?
What Keeps Bulimia Going?
Self-Monitoring Record (Universal)
Self-Monitoring Record (Universal)
What Keeps Anorexia Going?
What Keeps Anorexia Going?
Cognitive Behavioral Model of Perfectionism (Shafran, Egan, Wade, 2010)
Cognitive Behavioral Model of Perfectionism (Shafran, Egan, Wade, 2010)
Transdiagnostic Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Eating Disorders (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Transdiagnostic Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Eating Disorders (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Anorexia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Anorexia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Process Focused Case Formulation
Process Focused Case Formulation
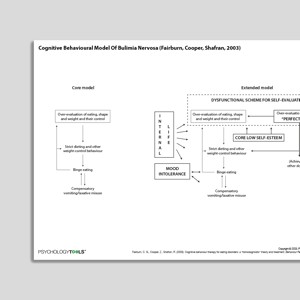
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Bulimia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Bulimia Nervosa (Fairburn, Cooper, Shafran, 2003)
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Assessment
-
Multidimensional perfectionism scale
| Hewitt, Flett | 1990
- Scale
-
Perfectionism Cognitions Inventory
| Flett, Hewitt, Blankstein, Gray | 1998
- Flett, G. L., Hewitt, P. L., Blankstein, K. R., & Gray, L. (1998). Psychological distress and the frequency of perfectionistic thinking. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(5), 1363-1381.
- Scale
- Scoring
-
The Almost Perfect Scale – Revised (APS-R)
| Slaney, Mobley, Trippi, Ashby, Johnson | 1996
- Slaney, R. B., Mobley, M., Trippi, J., Ashby, J. S., & Johnson, D. G. (1996). The Almost Perfect Scale–Revised. Unpublished manuscript, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park.
- Slaney, R. B., Rice, K. G., Mobley, M., Trippi, J., & Ashby, J. S. (2001). The revised Almost Perfect Scale. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 34, 130–145.
- Scale
- Website link
Information Handouts
York St John University
- Perfectionistic thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
-
Procrastination (Information Handouts)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions
- What Is Procrastination?
- Vicious Cycle of Procrastination
- Dismissing Procrastination Excuses
- Practical Strategies to Stop Procrastination
- Procrastination: Unhelpful Rules and Assumptions
- Tolerating Discomfort
- Action Plan
York St John University
- Measure of perfectionism
- The three flavors of perfectionism
- Perfectionism vs. doing things well
- Teachers guide to perfectionism
- Parents guide to perfectionism
- Coaches guide to perfectionism
- Perfectionism: A guide for when striving for perfection becomes unhealthy | Roz Shafran
Presentations
- OCD and perfectionism | Roz Shafran | 2011
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy for perfectionism | Martin Antony | 2015
- Comprehensive treatment of perfectionism | Martin Antony | 2013
Worksheets
- Procrastination (Worksheets) | Centre For Clinical Intervention
Recommended Reading
- Shafran, R., Coughtrey, A., & Kothari, R. (2016). New frontiers in the treatment of perfectionism. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 9(2), 156-170.
- Egan, S. J., Wade, T. D., & Shafran, R. (2011). Perfectionism as a transdiagnostic process: A clinical review. Clinical psychology review, 31(2), 203-212
What Is Perfectionism?
Disorders That Are Associated with Perfectionism, or in Which Perfectionism Is Elevated
Perfectionism is thought to contribute to be associated with or elevated in:obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)
social anxiety disorder
panic disorder
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
body dysmorphic disorder (BDD)
chronic fatigue syndrome
eating disorders
depression
bipolar disorder
suicidal ideation and behavior
Helpful Questions for Assessing Perfectionism
Some helpful questions for assessing perfectionism:Have you ever kept trying to meet your standards, even if this has meant that you have missed out on things?
What sorts of situations trigger feelings of distress when your standards are not met?
What do you think of people who do just enough to get by?
Do you ever feel a failure as a person because you haven’t met your goals?
Have you ever been told that your standards are too high?
In what ways do you compare yourself to others? How do you typically feel?
What kinds of domains must you be perfect in?
Are there any ways that perfectionism has been rewarded or praised in your life?
Treatment Approaches That Target Perfectionism
Shafran, Egan, and Wade (2010) published a cognitive behavioral model of perfectionism in which an individual’s self-worth is overly dependent on striving and achievement. They propose that this is maintained by both (1) revision of standards as insufficiently demanding when they are met, and (2) counterproductive behaviors and self-criticism when they are not met. There have been a number of small published studies that have examined the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy for the treatment of perfectionism, which show promisingly large effect sizes (e.g., Riley, Lee, Cooper, Fairburn, & Shafran, 2007; Steele & Wade, 2008).References
Burns, D. D. (1980). The perfectionist script for self-defeat. Psychology Today, November, 34–52.
Frost, R. O., Marten, P., Lahart, C., & Rosenblate, R. (1990). The dimensions of perfectionism. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 14(5), 449–468.
Riley, C., Lee, M., Cooper, Z., Fairburn, C. G., & Shafran, R. (2007). A randomised controlled trial of cognitive-behaviour therapy for clinical perfectionism: A preliminary study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 45(9), 2221–2231.
Shafran, R., Cooper, Z., & Fairburn, C. G. (2002). Clinical perfectionism: A cognitive–behavioural analysis. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 40(7), 773-791.
Shafran, R., Coughtrey, A., & Kothari, R. (2016). New frontiers in the treatment of perfectionism. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 9(2), 156-170.
Shafran, R., Egan, S., & Wade, T. (2018). Overcoming perfectionism: A self-help guide using scientifically supported cognitive behaviouraltechniques(2nd ed.). London: Robinson.
Steele, A. L., & Wade, T. D. (2008). A randomised trial investigating guided self-help to reduce perfectionism and its impact on bulimia nervosa: A pilot study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 46(12), 1316–1323.