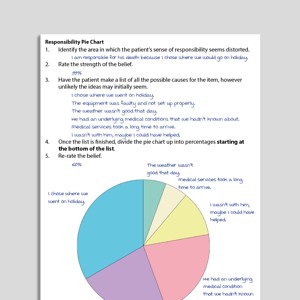
Shame
Shame is an emotion that often underpins difficulties including low self-esteem, depression, and PTSD. Highly shame-prone individuals sometimes find it difficult to benefit from traditional cognitive behavioral therapies and may benefit from a compassion-focused approach.
Early Maladaptive Schemas
Early Maladaptive Schemas
Audio Collection: Psychology Tools For Developing Self-Compassion
Audio Collection: Psychology Tools For Developing Self-Compassion
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
What Keeps Low Self-Esteem Going?
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Low Self-Esteem (Fennell, 1997)
Cognitive Behavioral Model Of Low Self-Esteem (Fennell, 1997)
Transdiagnostic Processes
Transdiagnostic Processes
A Guide To Emotions (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
A Guide To Emotions (Psychology Tools For Living Well)
Responses To Threat: Freeze, Appease, Flight, Fight
Responses To Threat: Freeze, Appease, Flight, Fight
Motivational Systems (Emotional Regulation Systems)
Motivational Systems (Emotional Regulation Systems)
What Is Compassion Focused Therapy (CFT)?
What Is Compassion Focused Therapy (CFT)?
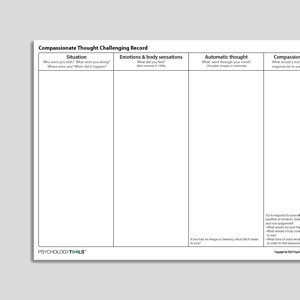
Compassionate Thought Challenging Record
Compassionate Thought Challenging Record
Coercive Methods For Enforcing Compliance
Coercive Methods For Enforcing Compliance
Barriers Abusers Overcome In Order To Abuse
Barriers Abusers Overcome In Order To Abuse
Before I Blame Myself And Feel Guilty
Before I Blame Myself And Feel Guilty
Links to external resources
Psychology Tools makes every effort to check external links and review their content. However, we are not responsible for the quality or content of external links and cannot guarantee that these links will work all of the time.
Guides and workbooks
- Combating self-criticism
- Abuse – Information For Adults Physically, Emotionally, Or Sexually Abused As Children (An NHS Self-Help Guide) | Lesley Maunder, Lorna Cameron | 2020
Information Handouts
- Shame handouts | Carol Morgaine
Presentations
- Compassion focused therapy: self-criticism | Paul Gilbert | 2017
- Shattered shame states and their repair | Judith Herman | 2007
- Empowerment and recovery for trauma survivors | Judith Herman
Self-Help Programmes
-
Building Self-Compassion (Workbook)
| Centre For Clinical Interventions | 2017
- Module 1: Understanding Self-Compassion
- Module 2: Barriers To Self-Compassion
- Module 3: Preparing For Self-Compassion
- Module 4: Compassionate Imagery
- Module 5: Self-Compassionate Thinking
- Module 6: Self-Compassionate Behavior
- Module 7: Self-Compassionate Living
Video
- The importance of soft toys | Donald Winnicott
Recommended Reading
- Fennell, Melanie JV. “Low self-esteem: a cognitive perspective.” Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 25.1 (1997): 1-26.
- Fennell, M. J. (1998). Cognitive therapy in the treatment of low self-esteem.Advances in Psychiatric Treatment,4(5), 296-304.
- Fennell, M. J. (2004). Depression, low self-esteem and mindfulness.Behaviour research and therapy,42(9), 1053-1067. Fennell, M. J. (1997). Low self-esteem: a cognitive perspective. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy, 25(1), 1-26.
- Gilbert, P. (2000). The relationship of shame, social anxiety and depression: The role of the evaluation of social rank.Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy: An International Journal of Theory & Practice,7(3), 174-189.
- Gilbert, P. (2009). Introducing compassion focused therapy. Advances in Psychiatric Treatment, 15, 199-208
- Veale, D., Gilbert, P. (2014). Body dysmorphic disorder: the functional and evolutionary context in phenomenology and a compassionate mind. Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, 3(2), 150-160
What Is Shame?
Signs and Symptoms Associated with Shame
Shame is an emotion of social comparison where an individual fears or anticipates eliciting disgust in others (Gilbert, 1992). Shame is experienced transdiagnostically and has been associated with increased symptom severity and poorer responses to treatment in conditions such as eating disorders (Troop, Allan, Serpell, & Treasure, 2008), PTSD (Dorahy et al., 2015), and depression (Andrews, 1995). Gilbert (1992, 1996) proposes that shame involves two components:external shame—thoughts and feelings about how one exists in the minds of others. For example thoughts that others view us having unattractive characteristics and may reject us;
internal shame—an awareness of how one exists in the minds of others. A focus on the self as flawed, bad, or inadequate (self-criticism).
Psychological Models and Theories of Shame
Paul Gilbert published an evolutionary account of shame which serves as the framework for compassion-focused therapy (CFT). This account argues that human beings have evolved to be regulated through social relationships. Shame means harboring fears that others will dislike or reject them, and experiencing high levels of shame means that individuals disconnect from and are less able to access soothing and regulation from others. Gilbert argues that “Shame is probably one of the most important inner experiences for creating the sense of difference and disconnection from others”(Gilbert, 2017).Evidence-Based Psychological Approaches for Working with Shame
Compassion-focused therapy (CFT) is regarded as a ‘third wave’ cognitive behavioral therapy. It was developed to help patients struggling with shame and self-criticism. Components of CFT interventions include psychoeducation about our ‘tricky minds,’ and the development of compassionate self-practice. The evidence base for CFT indicates that it is a promising intervention for shame and self-criticism (Leaviss & Uttley, 2015).Resources for Working with Shame
Psychology Tools resources available for working therapeutically with shame include:psychological models of shame and self-criticism
information handouts for shame and self-criticism
exercises for shame and self-criticism
CBT worksheets for shame and self-criticism
self-help programs for shame and self-criticism
References
Andrews, B. (1995). Bodily shame as a mediator between abusive experiences and depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104(2), 277–285.
Dorahy, M. J., Middleton, W., Seager, L., McGurrin, P., Williams, M., & Chambers, R. (2015). Dissociation, shame, complex PTSD, child maltreatment and intimate relationship self-concept in dissociative disorder, chronic PTSD and mixed psychiatric groups. Journal of Affective Disorders, 172, 195–203.
Gilbert, P. (1992). Depression: The evolution of powerlessness. New York: Routledge.
Gilbert, P. (2017). A brief outline of the evolutionary approach for compassion focused therapy. EC Psychology and Psychiatry, 3(6): 218–227.
Gilbert, P., Allan, S., & Goss, K. (1996). Parental representations, shame, interpersonal problems, and vulnerability to psychopathology. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy: An International Journal of Theory and Practice, 3(1), 23-34.
Leaviss, J., & Uttley, L. (2015). Psychotherapeutic benefits of compassion-focused therapy: An early systematic review. Psychological Medicine, 45(5), 927–945.
Troop, N. A., Allan, S., Serpell, L., & Treasure, J. L. (2008). Shame in women with a history of eating disorders. European Eating Disorders Review: The Professional Journal of the Eating Disorders Association, 16(6), 480–488.